Welcome to our blog, where we’ll explore the fascinating world of electrical pressure and its measurement. Have you ever wondered how electricity is measured? What units are used to quantify the “pressure” of electrical currents and fields? In this post, we’ll answer these questions and more.
Electrical pressure, commonly referred to as voltage, plays a crucial role in understanding and harnessing electricity. It determines the strength and flow of electric current in a circuit. To grasp the concept fully, it’s essential to delve into the fundamentals of voltage measurement and the units associated with it. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of electrical pressure and guide you through the terminology and principles involved.
Get ready to gain insights into the units used to measure electrical pressure, the historical journey of voltage measurement, and its relevance in various fields. Whether you’re a student, an electronics enthusiast, or simply curious about the world of electricity, this blog post will equip you with the knowledge you need to comprehend electrical pressure and how it is quantified. So let’s dive in and explore the electrifying realm of voltage measurement!
What Is Electrical Pressure Measured In
Have you ever wondered how electrical pressure is actually measured? Well, you’re in luck, because today we’re diving into the fascinating world of electrical pressure measurements. So grab your voltage meter and let’s get started!
The Mighty Volt: The Unit of Electrical Pressure
Why Volts and Not Something Else
When it comes to measuring electrical pressure, the unit that takes the crown is the volt. Named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, who invented the first electric battery, the volt has become the go-to unit for all things electrical pressure-related. And why not? It’s simple, elegant, and just rolls off the tongue.
Stepping Up: From Charges to Current
Now that we know the volt is our protagonist, let’s explore how it actually measures electrical pressure. Picture this: electricity flows through conductors like a waterfall cascading down a series of steps. These steps represent various electrical components, such as resistors or capacitors, that influence the flow of current.
Voltage Drop: A Not-So-Scary Movie
One key concept in understanding electrical pressure is the voltage drop. Just like when you open the faucet and the water pressure decreases as it flows through the pipes, electrical current experiences a drop in pressure as it encounters different components in a circuit. This voltage drop is precisely what the volt measures.
Multimeter Magic: An Electrical Wizard’s Wand
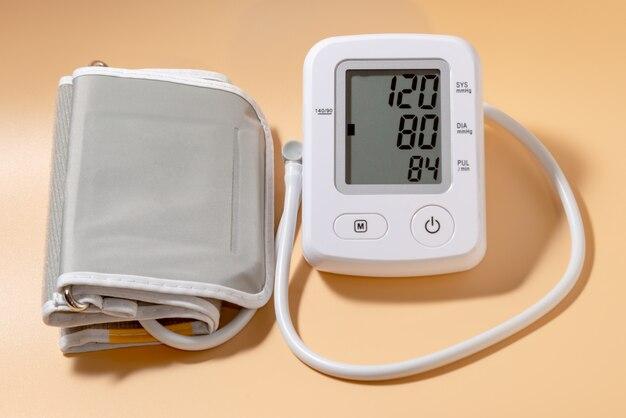
To measure electrical pressure in volts, you’ll need a trusty tool called a multimeter. This nifty device combines several essential measurement tools into one, like a Swiss Army knife for electricians. With its various settings, a multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance – all crucial aspects of understanding electrical pressure.
It’s All About Potential: Voltage and Energy
One thing to keep in mind is that electrical pressure (volts) is closely linked to energy. Just like a river flowing from a higher elevation to a lower one releases potential energy, electrical current flows from areas of higher voltage to lower voltage, releasing electrical energy in the process. So, in a way, volts are the currency of electrical energy!
Safety First: Take Proper Precautions
While measuring electrical pressure can be enlightening (pun intended), it’s essential to prioritize safety. Working with live circuits can be dangerous, so always make sure to take the necessary precautions. Safety goggles, insulated gloves, and a healthy dose of common sense are your best friends when it comes to electrical measurements.
So, my fellow curious minds, now you know what electrical pressure is measured in: the trusty volt! With our multimeters in hand, we can explore the electrifying world of volts, amps, and ohms. Just remember to stay safe and never underestimate the power of electrical pressure. May the volts be with you!
Keep an eye out for our next section, where we’ll dive into the exciting world of electric eels and their shocking adventures. Stay tuned, and stay electrified!
FAQ: What Is Electrical Pressure Measured In
How do you call the electric pressure
When it comes to electric pressure, it’s commonly referred to as voltage. Just like the pressure in a water pipe or the force exerted by air in a tire, voltage is the measure of electrical pressure in a circuit.
What’s current measured in
Electric current is measured in amperes, abbreviated as amps. It represents the flow of electric charge in a circuit. So, when you hear someone talk about amps, they’re referring to the amount of current flowing through a conductor.
How was voltage first measured
Voltage was first measured back in the late 18th century by an Italian physicist named Alessandro Volta. He invented the first battery, known as the Voltaic pile, and used it to measure voltage.
What is electric field Class 12
In Class 12 Physics or Electrical Engineering courses, students encounter the concept of electric fields. Electric fields describe the region around a charged object where another charged object would experience a force. It’s an important concept in understanding the behavior of electrical charges.
How do you measure electric current in a circuit
To measure electric current in a circuit, you would typically use an ammeter. An ammeter is a device that connects in series to the circuit and measures the flow of current. It’s like a traffic cop for electrons, telling you how many are passing through a specific point in a given time.
What is an electric pressure
Electric pressure, also known as voltage, refers to the push or force that drives electric current through a circuit. It’s the driving force that allows the electrons to flow in a specific direction, creating the electric current we harness for various purposes.
What is current and How is It measured
Current refers to the flow of electric charge in a circuit. It’s the movement of electrons through a conductor. As mentioned earlier, current is measured in amperes. You can measure it using an ammeter, which is placed in series with the circuit to measure the flow of electrons.
Is voltage electrical pressure called
Yes, voltage is the term commonly used to refer to electric pressure. It’s like the “force” behind the flow of electric current. So, the next time someone talks about voltage, remember, they’re talking about electrical pressure.
How is voltage determined in electric pressure
Voltage in electric pressure is determined by measuring the potential difference between two points in a circuit. This potential difference creates the push or pressure for the electrons to move from one point to another. By measuring this difference, we can determine the voltage.
Can batteries supply electrical pressure
Absolutely! Batteries are great examples of devices that supply electrical pressure or voltage. They do so by converting chemical energy into electrical energy, providing the driving force necessary for the flow of current in a circuit.
What do VI and R stand for in Ohm’s law
In Ohm’s law, V stands for voltage, I stands for current, and R stands for resistance. Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit.
Why is voltage called pressure
Voltage is referred to as pressure because it’s the driving force behind the flow of electrical current. Just like pressure pushes water through a pipe, voltage pushes electrons through a conductor, enabling the flow of electricity.
How is electrostatic pressure calculated
Electrostatic pressure, or voltage, can be calculated by dividing the work done to move a charge between two points by the amount of charge moved. This calculation helps determine the potential difference between the two points.
What is the electric field formula
The electric field at a point in space can be calculated using the formula:
E = F / q,
where E represents the electric field, F represents the force experienced by the charge at that point, and q represents the magnitude of the charge.
How is voltage measured
Voltage can be measured using a voltmeter, which is connected in parallel to the circuit. The voltmeter measures the potential difference between two points and gives the voltage reading in volts (V).
What is the electrical unit of current
The electrical unit of current is the ampere (A). It represents the flow of one coulomb of charge per second through a conductor.
How do I calculate current
You can calculate current by dividing the amount of charge passing through a point in a circuit by the time it takes for that charge to pass. The formula is:
I = Q / t,
where I represents current, Q represents charge, and t represents time.
What is the value of k in electrostatics
The value of k, known as the Coulomb’s constant, in electrostatics is 8.99 x 10^9 N m^2/C^2. This constant is used in calculations involving electrical forces between charged objects.
What is Ohm’s law Bitesize
Ohm’s law is a fundamental principle in electrical circuits that states the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It can be summarized in a simple formula:
V = I x R,
where V represents voltage, I represents current, and R represents resistance. Ohm’s law Bitesize is a bite-sized explanation of this important electrical concept.
What is Ohm’s law triangle
The Ohm’s law triangle is a visual representation of Ohm’s law formula, V = I x R. It helps determine the value of the missing variable by covering it up and rearranging the formula to solve for the desired variable. The triangle has three sides, with V on top, I on the left, and R on the right, forming a simple and handy tool for calculations.
In which unit can we measure electrical pressure
Electrical pressure, or voltage, can be measured in volts (V). It’s the unit used worldwide to quantify the potential difference that drives the flow of electric current.